ESTECH.PS-X
Feature
Typically calculate elastic vibration of an automobile reciprocate engine under operating condition in a frequency domain very rapidly, which is a unique and innovative FE simulation software.
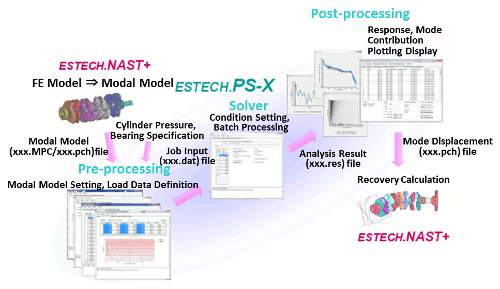
- When an engine is running, a rotating crankshaft and non-rotating cylinder block are dynamically coupled. In order to predict this phenomenon, it is very common to solve the CAE model in a time domain by kinematic mechanism software including elastic crankshaft and cylinder block models. However, the time domain analytical method takes much longer computational time, that is a bottle neck for the engine noise and vibration analysis. Now, a new technology is created by the company, which crankshaft and cylinder block are coupled in frequency domain. (It is patented in Japan in Aug. 2003, Patent#:5352026)
- The method enables engineer to analyze engine elastic vibration in a significantly short period of time. A benchmarking test by the company revealed the new method was 150 times faster than the legacy time domain method as well as computation was quite stable.
- The software works together with ESTECH.NAST+ and MSC Nastran, which makes it possible to conduct modes and input forces contribution analyses for the effective engine design parameter study.
- This approach is also available to simulate centrifugal and Coriolis forces generated by crankshaft rotation
- Furthermore, pre- and post-processor interfaces for engine vibration analysis are available.
1 : Trial analysis by test model
-
Computational Condition : 3000rpm, including centrifugal force of crankshaft and applying only 4th order of loading to piston pin
Bearing Model : linear oil film model describes by Reynold's equation
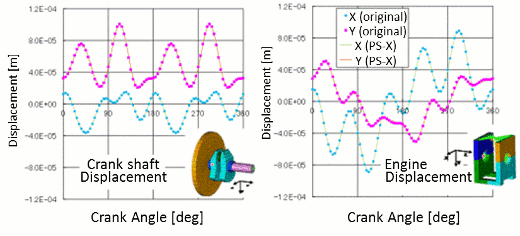
- Output from the software is identical to the one from legacy kinematic mechanism analysis considering elasticity of the structure. The above figures show comparison between the output from ESTECH.PS-X and one from Adams/Flex
-
Computational time comparison on Windows 32 bit PC
- ESTECH.PS-X: 4 sec
- Adams/Flex: 600 sec. -
Order tracking analysis of vibration at monitoring points( RSS values of 3 translational directions )
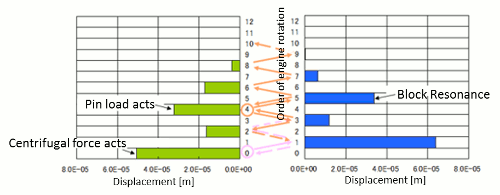
- The different orders of vibration are coupled between engine crankshaft and cylinder block. ESTECH.PS-X clarifies the cause of engine vibration utilizing original functions which analyze orders of input forces, input force location contribution as well as natural modes contribution.
2 : Trial analysis by solver
-
The following figure and table show a trial analysis result of the developed solver applying to power plant which is standard size of FE model for NV analysis and checked computational time of the solver.
Computational Specification
ENG Model
ENG Cubic Size
DOF of FE model
Number of crankshaft modes
Number of ENG structural modesInline 4 cylinder
2000 cc
around 6,000,000 DOF
81(Natural modes :41/RESVEC: 40)
239(Natural modes: 163/RESVEC:76)Operating Condition
Max Frequency
CPU
DOF of Response pt.
Computational time by PS-X solver3000rpm WOT
1000 Hz (20th order)
Windows7 64bit/CPU 3.6GHz/16GB RAM
45 DOF
Approximately12 sec※ -
PS-X solver calculates engine vibration under operating condition very quickly on Windows PC.
* This time excludes modal model creating time by ESTECH.NAST+. Furthermore, use of ESTECH.NAST+ on server of MSC Nastran analysis is highly recommended.。
3 : Trial of mode contribution analysis
-
The mode contribution analysis is one of the ESTECH.PS-X post processing functions.
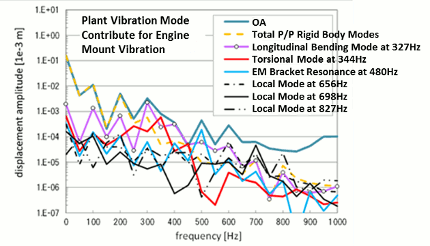
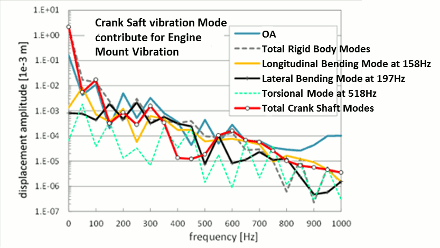
- The mode contribution analysis assists to develop countermeasures in order to improve the problems by identifying natural modes which have significant contribution to engine structural vibration.
- In addition to the above, the analysis also identifies quantitatively how each natural mode of a crank shaft affects to engine structural modes, which is compared with each other for design study.
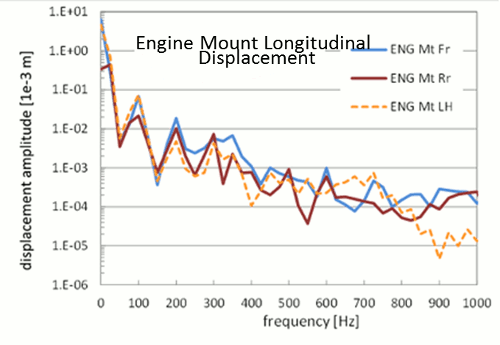
4 : Visualization of operational vibration mode
-
Recovery is available for entire engine vibration under arbitrary operating conditions or at any frequency ranges.
RWD 4Cylinder LH Mount / 3200rpm / WOT / Vibration recovery in 550Hz to 650Hz

 Recovery
Recovery

- Large deformation near 5th journal is observed which causes the excitation force on engine block.
5 : Response surface analysis
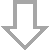
- Response surface of engine vibration is calculated by changing modal stiffness and mass with multiple level.
- The response surface analysis creates the most relevant design guidelines.
-
The large amount of computation due to the combination of design parameters can be conducted with high speed, which is hard to be executed by traditional analytical method in time domain.
(This case study : Calculation : 2100 times, 1month ->7 hours)
Change modal parameter (M/K)of crank lateral bend
Lateral Bend 252Hz
Overview
| Name | ESTECH.PS-X |
|---|---|
| Functions |
|
| Computational Condition |
|
| Engine Type |
|
Contact
Please feel free to contact for further information
ESTECH Corp. Engineering Department
E-mail:info@estech.co.jp
TEL:81-45-661-1661 / FAX:81-45-661-1664
*The name of company and/or individual product name mentioned above are either trademark or registered trademark.


